gRPC(Go)入门教程(七)—利用Gateway同时提供HTTP和RPC服务
1. 概述
gRPC 系列相关代码见 Github
gRPC-Gateway 是Google protocol buffers compiler(protoc)的一个插件。读取 protobuf 定义然后生成反向代理服务器,将 RESTful HTTP API 转换为 gRPC。
换句话说就是将 gRPC 转为 RESTful HTTP API。
源自 coreos 的一篇博客,转载到了 gRPC 官方博客 gRPC with REST and Open APIs。
etcd v3 改用 gRPC 后为了兼容原来的 API,同时要提供 HTTP/JSON 方式的API,为了满足这个需求,要么开发两套 API,要么实现一种转换机制,他们选择了后者,而我们选择跟随他们的脚步。
架构如下
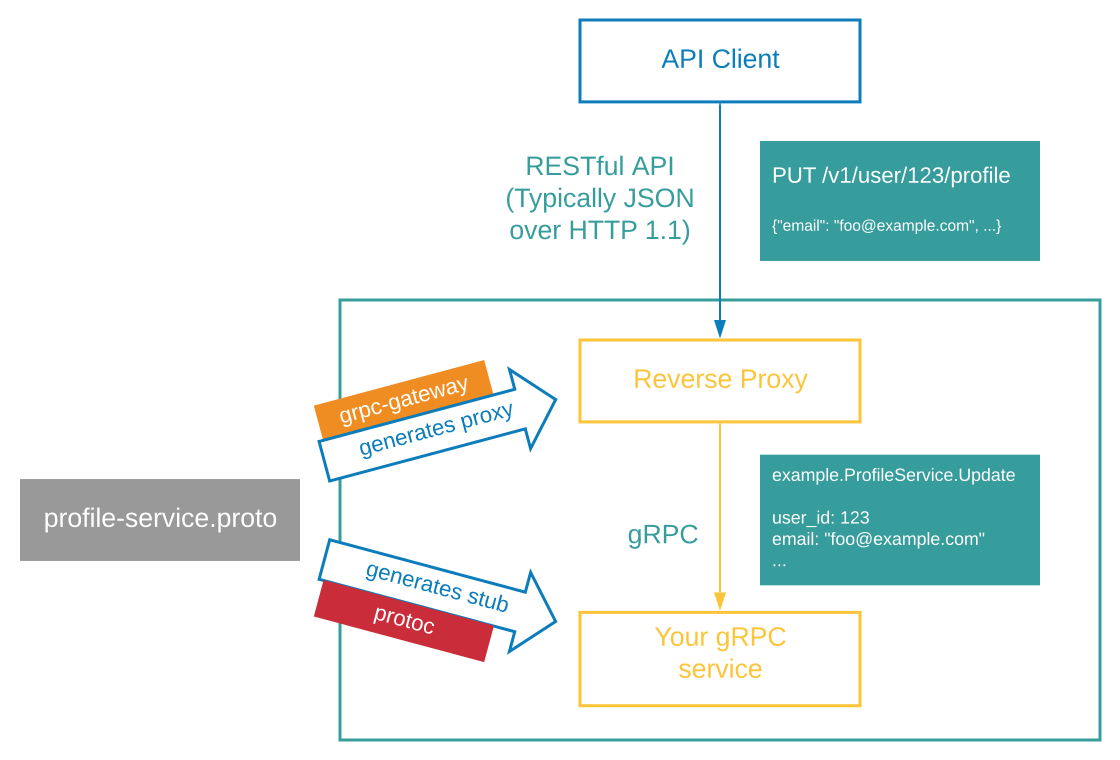
当 HTTP 请求到达 gRPC-Gateway 时,它将 JSON 数据解析为 Protobuf 消息。然后,它使用解析的 Protobuf 消息发出正常的 Go gRPC 客户端请求。Go gRPC 客户端将 Protobuf 结构编码为 Protobuf 二进制格式,然后将其发送到 gRPC 服务器。gRPC 服务器处理请求并以 Protobuf 二进制格式返回响应。Go gRPC 客户端将其解析为 Protobuf 消息,并将其返回到 gRPC-Gateway,后者将 Protobuf 消息编码为 JSON 并将其返回给原始客户端。
简单来说就是生成了一个 HTTP 服务,在具体处理逻辑中去请求 gRPC 服务。
2. 环境准备
环境主要分为 3 部分:
1)Protobuf 相关 Go Protocol buffer compile(protoc) Go Plugins 2)gRPC相关 gRPC Lib gRPC Plugins 3)gRPC-Gateway 相关 gRPC-Gateway
1. Protobuf
具体见 Protobuf 章节
2. gRPC
具体见 gRPC章节
3. gRPC-Gateway
gRPC-Gateway 只是一个插件,只需要安装一下就可以了。
go get github.com/grpc-ecosystem/grpc-gateway/v2/protoc-gen-grpc-gateway
4. 整体流程
大致就是以 .proto 文件为基础,编写插件对 protoc 进行扩展,编译出不同语言不同模块的源文件。
1)首先定义 .proto 文件;
2)然后由 protoc 将 .proto 文件编译成 protobuf 格式的数据;
3)将 2 中编译后的数据传递到各个插件,生成对应语言、对应模块的源代码。
Go Plugins 用于生成 .pb.go 文件
gRPC Plugins 用于生成 _grpc.pb.go
gRPC-Gateway 则是 pb.gw.go
其中步骤2和3是一起的,只需要在 protoc 编译时传递不同参数即可。
比如以下命令会同时生成 Go、gRPC 、gRPC-Gateway 需要的 3 个文件。
protoc --go_out . --go-grpc_out . --grpc-gateway_out . hello_world.proto
3. 例子
本文所有代码都在这里 Github。
首先确保自己的环境是ok的,具体如下:
1)执行 protoc --version 能打印出版本信息; 2)$GOPATH/bin 目录下有 protoc-gen-go、protoc-gen-go-grpc、protoc-gen-grpc-gateway 这三个可执行文件。
1. gRPC 部分
1)创建.proto文件
创建一个 hello_world.proto 文件,内容如下
具体目录为:proto/helloworld/hello_world.proto
syntax = "proto3";
option go_package=".;proto";
package helloworld;
// The greeting service definition
service Greeter {
// Sends a greeting
rpc SayHello (HelloRequest) returns (HelloReply) {}
}
// The request message containing the user's name
message HelloRequest {
string name = 1;
}
// The response message containing the greetings
message HelloReply {
string message = 1;
}
2) 生成 Go subs
使用 protoc 编译生成不同模块的源文件,具体命令如下:
lixd@17x:~/17x/projects/grpc-go-example/features$ protoc --proto_path=./proto \
--go_out=./proto --go_opt=paths=source_relative \
--go-grpc_out=./proto --go-grpc_opt=paths=source_relative \
./proto/helloworld/hello_world.proto
具体 protoc 信息可查看 protobuf 章节。
会生成 *.pb.go 和 *_grpc.pb.go 两个文件。
3) Server
main.go内容如下:
package main
import (
"context"
"flag"
"fmt"
"log"
"net"
pb "github.com/lixd/grpc-go-example/features/proto/helloworld"
"google.golang.org/grpc"
)
var port = flag.Int("port", 50051, "the port to serve on")
type server struct {
pb.UnimplementedGreeterServer
}
func (s *server) SayHello(ctx context.Context, in *pb.HelloRequest) (*pb.HelloReply, error) {
return &pb.HelloReply{Message: "hello " + in.Name }, nil
}
func main() {
// Create a gRPC server object
s := grpc.NewServer()
// Attach the Greeter service to the server
pb.RegisterGreeterServer(s, &server{})
// Serve gRPC Server
lis, err := net.Listen("tcp", fmt.Sprintf(":%d", *port))
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("failed to listen: %v", err)
}
log.Println("Serving gRPC on 0.0.0.0" + fmt.Sprintf(":%d", *port))
if err := s.Serve(lis); err != nil {
log.Fatalf("failed to serve: %v", err)
}
}
4)Client
main.go内容如下:
package main
import (
"log"
"golang.org/x/net/context"
"google.golang.org/grpc"
pb "i-go/grpc/gateway/proto/helloworld"
)
const (
address = "localhost:8080"
defaultName = "world"
)
func main() {
conn, err := grpc.Dial(address, grpc.WithInsecure(), grpc.WithBlock())
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
defer conn.Close()
c := pb.NewGreeterClient(conn)
r, err := c.SayHello(context.Background(), &pb.HelloRequest{Name: defaultName})
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("could not greet: %v", err)
}
log.Printf("Greeting: %s", r.Message)
}
5)run
到此分别运行 server.go、client.go ,一个简单的 gRPC demo 就跑起来了。
lixd@17x:~/17x/projects/grpc-go-example/features/gateway/server$ go run main.go 2021/01/30 10:15:53 Serving gRPC on 0.0.0.0:50051
lixd@17x:~/17x/projects/grpc-go-example/features/gateway/client$ go run main.go 2021/01/30 10:17:23 Greeting: hello world
2. gRPC-Gateway 部分
接下来需要对之前的 gRPC 代码进行调整,使其能对外提供 RESTful HTTP API。
1)修改 .proto 文件
在原有基础上,添加 gRPC-Gateway 注解。修改后内容如下:
syntax = "proto3";
option go_package = "github.com/lixd/grpc-go-example/features/proto/echo";
package helloworld;
import "google/api/annotations.proto";
service Greeter {
rpc SayHello (HelloRequest) returns (HelloReply) {
option (google.api.http) = {
get: "/v1/greeter/sayhello"
body: "*"
};
}
}
message HelloRequest {
string name = 1;
}
message HelloReply {
string message = 1;
}
主要修改了两个地方
第一步引入annotations.proto
import "google/api/annotations.proto";
引入annotations.proto文件,因为添加的注解依赖该文件。
该文件需要手动从 https://github.com/googleapis/googleapis 仓库下载到自己的项目中。 该文件需要手动从 https://github.com/googleapis/googleapis 仓库下载到自己的项目中。 该文件需要手动从 https://github.com/googleapis/googleapis 仓库下载到自己的项目中。
下载链接如下:
https://github.com/googleapis/googleapis/tree/master/google/api
复制后的目录结构如下:
proto
├── google
│ └── api
│ ├── annotations.proto
│ └── http.proto
└── helloworld
└── hello_world.proto
第二步增加 http 相关注解
rpc SayHello (HelloRequest) returns (HelloReply) {
option (google.api.http) = {
get: "/v1/greeter/sayhello"
body: "*"
};
}
每个方法都必须添加 google.api.http 注解后 gRPC-Gateway 才能生成对应 http 方法。
其中post为 HTTP Method,即 POST 方法,/v1/greeter/sayhello 则是请求路径。
更多语法看这里:
https://github.com/googleapis/googleapis/blob/master/google/api/http.proto
2)再次编译
增加 –grpc-gateway_out
lixd@17x:~/17x/projects/grpc-go-example/features$ protoc --proto_path=./proto \ --go_out=./proto --go_opt=paths=source_relative \ --go-grpc_out=./proto --go-grpc_opt=paths=source_relative \ --grpc-gateway_out=./proto --grpc-gateway_opt=paths=source_relative \ ./proto/helloworld/hello_world.proto
如果提示
gogoproto/gogo.proto: File not found.
下载
https://github.com/gogo/protobuf #将里面的gogoproto 文件夹放置proto目录下
本次会多生成一个gw.pb.go 文件,用于启动 HTTP 服务。
其中–proto_path=./proto用于指定 import 文件路径(默认为{$pwd}),即前面引入的google/api/annotations.proto文件的位置。
3)调整 Server
在原有 gRPC 基础上在启动一个 HTTP 服务。
package main
import (
"context"
"flag"
"fmt"
"log"
"net"
"net/http"
"github.com/grpc-ecosystem/grpc-gateway/v2/runtime"
pb "github.com/lixd/grpc-go-example/features/proto/helloworld"
"google.golang.org/grpc"
)
var port = flag.Int("port", 50051, "the port to serve on")
var restful = flag.Int("restful", 8080, "the port to restful serve on")
type server struct {
pb.UnimplementedGreeterServer
}
func (s *server) SayHello(ctx context.Context, in *pb.HelloRequest) (*pb.HelloReply, error) {
return &pb.HelloReply{Message: "hello " + in.Name}, nil
}
func main() {
// Create a gRPC server object
s := grpc.NewServer()
// Attach the Greeter service to the server
pb.RegisterGreeterServer(s, &server{})
// Serve gRPC Server
lis, err := net.Listen("tcp", fmt.Sprintf(":%d", *port))
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("failed to listen: %v", err)
}
log.Println("Serving gRPC on 0.0.0.0" + fmt.Sprintf(":%d", *port))
go func() {
if err := s.Serve(lis); err != nil {
log.Fatalf("failed to serve: %v", err)
}
}()
// 2. 启动 HTTP 服务
// Create a client connection to the gRPC server we just started
// This is where the gRPC-Gateway proxies the requests
conn, err := grpc.Dial(
"localhost:50051",
grpc.WithInsecure(),
)
if err != nil {
log.Fatalln("Failed to dial server:", err)
}
gwmux := runtime.NewServeMux()
// Register Greeter
err = pb.RegisterGreeterHandler(context.Background(), gwmux, conn)
if err != nil {
log.Fatalln("Failed to register gateway:", err)
}
gwServer := &http.Server{
Addr: fmt.Sprintf(":%d", *restful),
Handler: gwmux,
}
log.Println("Serving gRPC-Gateway on http://0.0.0.0"+fmt.Sprintf(":%d", *restful))
log.Fatalln(gwServer.ListenAndServe())
}
主要增加了 启动 HTTP 服务的部分。
4)run
运行并测试效果。
lixd@17x:~/17x/projects/grpc-go-example/features/gateway/server$ go run main.go 2021/01/30 10:32:15 Serving gRPC on 0.0.0.0:50051 2021/01/30 10:32:15 Serving gRPC-Gateway on http://0.0.0.0:8080
gRPC 请求
lixd@17x:~/17x/projects/grpc-go-example/features/gateway/client$ go run main.go 2021/01/30 10:32:18 Greeting: hello world
HTTP 请求
$ curl -k http://localhost:8080/v1/greeter/sayhello?name=world
{"message":"hello world"}
将 GET 请求修改为 POST,只需要修改 proto 文件中的注释并重新编译即可
option (google.api.http) = {
post: "/v1/greeter/sayhello",
body: "*"
};
同时还增加了 body 字段用于接收http request body 中的参数,不指定则无法接收。
编译后重启服务端,测试如下:
$ curl -X POST -k http://localhost:8080/v1/greeter/sayhello -d '{"name": "world"}'
{"message":"hello world"}
到此为止就同时启动了 gPRC 服务和 HTTP 服务。
3. 源码分析
首先建立 gRPC 连接,然后New 一个 ServeMux 接着调用了pb.RegisterGreeterHandler() 方法,最后就启动了一个 HTTP 服务。
很明显重点就是pb.RegisterGreeterHandler()这个方法,该方法就是 gRPC-Gateway 生成的。
具体如下:
func RegisterGreeterHandler(ctx context.Context, mux *runtime.ServeMux, conn *grpc.ClientConn) error {
return RegisterGreeterHandlerClient(ctx, mux, NewGreeterClient(conn))
}
func RegisterGreeterHandlerClient(ctx context.Context, mux *runtime.ServeMux, client GreeterClient) error {
mux.Handle("POST", pattern_Greeter_SayHello_0, func(w http.ResponseWriter, req *http.Request, pathParams map[string]string) {
ctx, cancel := context.WithCancel(req.Context())
defer cancel()
inboundMarshaler, outboundMarshaler := runtime.MarshalerForRequest(mux, req)
rctx, err := runtime.AnnotateContext(ctx, mux, req, "/helloworld.Greeter/SayHello")
if err != nil {
runtime.HTTPError(ctx, mux, outboundMarshaler, w, req, err)
return
}
resp, md, err := request_Greeter_SayHello_0(rctx, inboundMarshaler, client, req, pathParams)
ctx = runtime.NewServerMetadataContext(ctx, md)
if err != nil {
runtime.HTTPError(ctx, mux, outboundMarshaler, w, req, err)
return
}
forward_Greeter_SayHello_0(ctx, mux, outboundMarshaler, w, req, resp, mux.GetForwardResponseOptions()...)
})
return nil
}
可以看到直接通过 mux.Handle 注册了一个 HTTP 路由。
mux.Handle("POST", pattern_Greeter_SayHello_0, func(w http.ResponseWriter, req *http.Request, pathParams map[string]string) {
})
HTTP Method 为 POST 就是前面在 .proto 文件中指定的。
Pattern(路由信息)pattern_Greeter_SayHello_0 也是前面在 .proto 文件中指定的。具体如下:
var (
pattern_Greeter_SayHello_0 = runtime.MustPattern(runtime.NewPattern(1, []int{2, 0, 2, 1, 2, 2}, []string{"v1", "example", "echo"}, ""))
)
具体 Handler 的逻辑部分主要是这个方法
resp, md, err := request_Greeter_SayHello_0(rctx, inboundMarshaler, client, req, pathParams)
具体如下:
func request_Greeter_SayHello_0(ctx context.Context, marshaler runtime.Marshaler, client GreeterClient, req *http.Request, pathParams map[string]string) (proto.Message, runtime.ServerMetadata, error) {
var protoReq HelloRequest
var metadata runtime.ServerMetadata
newReader, berr := utilities.IOReaderFactory(req.Body)
if berr != nil {
return nil, metadata, status.Errorf(codes.InvalidArgument, "%v", berr)
}
if err := marshaler.NewDecoder(newReader()).Decode(&protoReq); err != nil && err != io.EOF {
return nil, metadata, status.Errorf(codes.InvalidArgument, "%v", err)
}
msg, err := client.SayHello(ctx, &protoReq, grpc.Header(&metadata.HeaderMD), grpc.Trailer(&metadata.TrailerMD))
return msg, metadata, err
}
可以看到最后是通过 gRPC client 发起的调用
msg, err := client.SayHello(ctx, &protoReq, grpc.Header(&metadata.HeaderMD), grpc.Trailer(&metadata.TrailerMD))
到这里可以发现 gRPC-Gateway 的具体流程和之前的描述是一致的。